Table of Contents
Bariatric surgery has become an increasingly popular option for individuals seeking a solution to obesity and weight-related health issues. You may wonder what makes this surgical procedure work so effectively, especially when many people have tried non-surgical methods without success. The answer lies in the complex interplay between physiological, metabolic, and hormonal factors that bariatric surgery addresses.
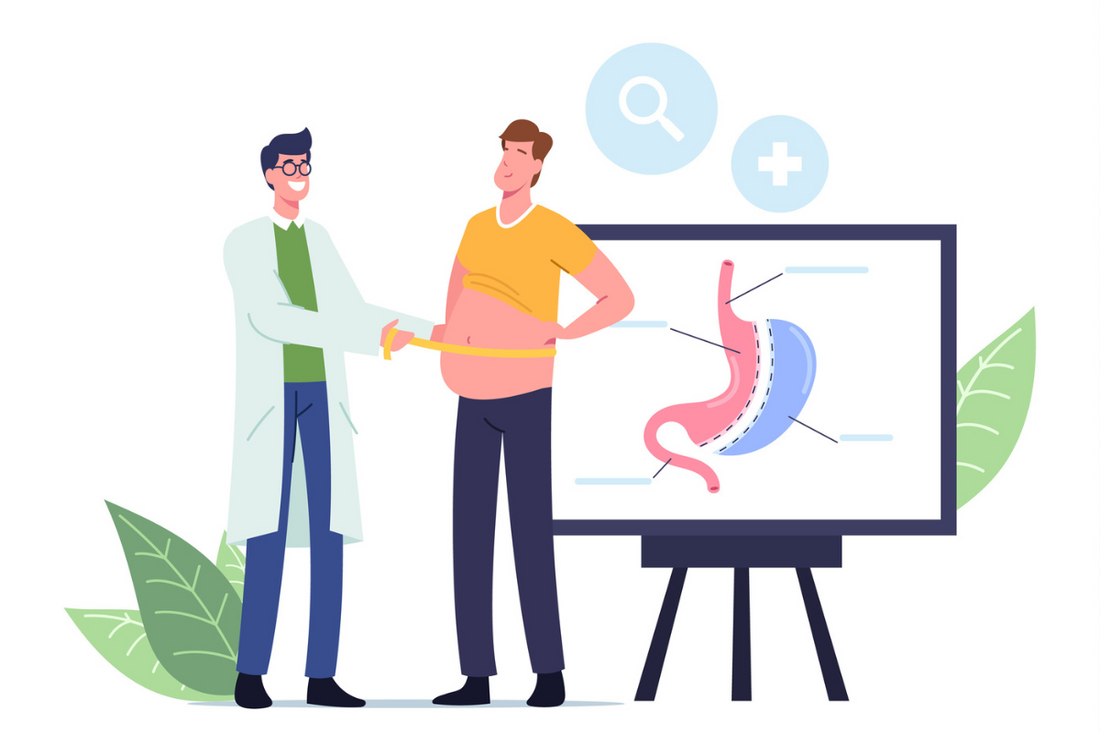
When you undergo bariatric surgery, your digestive system is altered in ways that promote weight loss. The most common procedures – such as gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric banding – work by reducing the stomach size or rerouting the small intestine. As a result, you experience a decreased appetite, a reduced capacity for food intake, and changes in the way your body absorbs and digests nutrients.
In addition to these physical modifications, bariatric surgery also impacts your body's hormonal balance. Research has shown that the surgery can improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, which in turn help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk for type 2 diabetes. Moreover, appetite-regulating hormones like ghrelin and leptin are also affected, promoting satiety and improved weight management.
How Does Bariatric Surgery Work?

Bariatric surgery is designed to help you lose weight by altering your digestive system. There are different types of bariatric surgeries, each with its own approach to achieving weight loss. In this section, we will discuss the most common types of bariatric surgery and how they work.
Sleeve Gastrectomy: Also known as gastric sleeve surgery, this procedure involves a surgeon removing a large portion of your stomach, leaving behind a smaller, banana-shaped pouch. This reduces the amount of food you can consume and, as a result, leads to weight loss. Additionally, the surgery affects your metabolism by reducing the production of hunger-inducing hormones in the stomach.
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass: In this surgery, a small pouch is created by stapling off a portion of the stomach. The surgeon then connects this small pouch to the lower part of your small intestine, bypassing a significant portion of your stomach and the first part of the small intestine called the duodenum. This procedure results in weight loss by reducing the amount of food you can eat and the number of calories your body absorbs.
Duodenal Switch: This is a combination of sleeve gastrectomy and intestinal bypass. In the first part of the procedure, a gastric sleeve is performed, restricting the amount of food you can eat. Then, the duodenal switch is performed, where a large portion of the small intestine is bypassed to limit calorie absorption. Additionally, the biliopancreatic diversion alters the way bile and digestive enzymes break down food, further promoting weight loss.
Gastric Banding: This procedure involves placing an adjustable silicone band around the upper part of your stomach to create a smaller pouch. The size of the opening between the pouch and the rest of the stomach can be adjusted by filling or removing saline from the band. This results in weight loss by restricting the volume of your food intake.
Before undergoing any bariatric surgery, you will have a thorough evaluation by healthcare professionals to determine if you are a suitable candidate for the procedure. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH) guidelines, candidates must typically have a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher or a BMI of 35 or higher with obesity-related health issues.
All bariatric surgeries are performed under general anesthesia. After the surgery, you will be required to follow a specific post-operative diet and maintain regular check-ups with your healthcare team. It is essential to remember that bariatric surgery is not a quick fix; it is a tool that can help you achieve long-term weight loss when combined with healthy lifestyle changes.
Why Does Bariatric Surgery Work?

Bariatric surgery is a highly effective treatment for obesity and its related health problems. It works by altering your digestive system to help you lose weight and maintain a healthier lifestyle. Several factors contribute to its success.
Factors Of Bariatric Surgery Success
Firstly, bariatric surgery helps you consume fewer calories. By reducing the size of your stomach or bypassing part of your small intestine, the procedure limits the amount of food you can eat at one time. This leads to a significant decrease in your daily calorie intake, promoting weight loss.
Additionally, bariatric surgery impacts the hormones that regulate your appetite and metabolism. The surgery affects gut hormones such as ghrelin and GLP-1, which control hunger and satiety. As a result, you may experience less frequent and intense hunger, making it easier to follow a balanced diet.
Another factor is the improvement in your body's ability to utilize calories and nutrients. Certain types of bariatric procedures, like the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, alter the way your body absorbs and metabolizes food. This can lead to increased energy expenditure, further promoting weight loss.
Lastly, the weight loss achieved through bariatric surgery often leads to improvements in obesity-related health problems. You may experience a reduction in conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea, leading to an overall better quality of life.
In summary, bariatric surgery works by targeting multiple aspects of obesity, including calorie intake, hormone regulation, and metabolism. By addressing these factors, the procedure helps you achieve and maintain a healthier weight and improve related health problems. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice on whether bariatric surgery is the right choice for you.
What is the Success Rate for Bariatric Surgery?

When considering bariatric surgery, it is important to understand its success rate. The American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) has provided data on the long-term success of various bariatric procedures. It is worth noting that success is typically measured in terms of weight loss and improvements in health.
One standard metric for evaluating success is the percentage of excess weight lost. Excess weight is the difference between a person's current body mass index (BMI) and their ideal BMI (usually set at 25). For example, if your current BMI is 40 and your ideal BMI is 25, your excess weight is 15 BMI points.
Most bariatric surgeries show a high degree of success; patients generally lose a significant amount of their excess weight. Research suggests that, on average, patients lose 50-75% of their excess weight within two years following the procedure.
Gastric bypass is one of the most common procedures and is known for its long-term success rate. Patients typically lose 60-80% of their excess weight within a year, and most maintain this weight loss over the years. Sleeve gastrectomy patients also experience a high level of success, with an average loss of 50-70% of excess weight.
Adjustable gastric banding is another option, but it has a lower success rate compared to gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy. Patients tend to lose 40-60% of their excess weight; however, the weight loss can be highly variable, and some individuals may only lose a minimal amount.
Aside from weight loss, bariatric surgery patients often see improvements in obesity-related comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea. These improvements contribute to an overall better quality of life and a reduced risk for serious health complications.
It is essential to remember that individual results will vary, and long-term success depends on a person's commitment to lifestyle changes, including diet, exercise, and adherence to follow-up care. Your healthcare team will work closely with you to ensure the best possible outcome from your bariatric surgery.
Why Do You Lose Weight So Fast with Bariatric Surgery?

Bariatric surgery is a highly effective method for achieving significant weight loss. When you undergo weight loss surgery, your body undergoes numerous changes, which contribute to a rapid reduction in excess weight. In this section, we'll explore the factors that contribute to quick weight loss following bariatric surgery.
Factors That Contribute To Quick Weight Loss
- First, bariatric surgery helps you reduce your calorie intake. By altering the structure of your stomach or digestive tract, the surgery limits the amount of food you can comfortably consume at any given time. This ultimately leads to lower daily calorie consumption, which is essential for weight loss. As you consume fewer calories, your body taps into stored energy, burning fat to meet its energy requirements.
- Second, your metabolism may change after bariatric surgery. While the specific changes vary depending on the type of procedure, certain surgeries alter the levels of hormones that regulate your appetite and metabolic rate. As a result, you may experience a temporary increase in metabolism, allowing your body to burn more calories at rest. This helps accelerate the rate at which you lose excess weight.
- Bariatric surgery also promotes weight loss through malabsorption. Some procedures, such as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, involve rearranging the intestinal tract to inhibit the absorption of calories and nutrients. When some consumed calories bypass the small intestine, the body does not absorb them and thus are not added to your total caloric intake.
- Additionally, weight loss surgery can positively affect your attitude towards food and eating habits. As you begin to see results quickly after the procedure, you may feel more motivated to maintain a healthy diet and exercise regimen. This can create a positive feedback loop that encourages weight loss and helps you achieve your goals faster.
In summary, rapid weight loss after bariatric surgery can be attributed to various factors, including reduced calorie intake, changes in metabolism, malabsorption, and improvements in eating behavior. By understanding these factors, you can effectively manage your expectations and work towards achieving sustainable weight loss.
Why Bariatric Surgery Works When Diets Don't?
When it comes to battling obesity, you might have tried multiple diets and lifestyle changes but found them to be insufficient or difficult to maintain. As a result, you may now be considering bariatric surgery as an alternative method for weight loss. Understanding why bariatric surgery works when diets don't may help you feel more confident in your decision.
Bariatric Surgery Vs Diet Food
Firstly, bariatric surgery directly alters your gastrointestinal system, primarily by reducing the stomach size. This limits the amount of food you can consume at once, helping you feel full faster with fewer calories. In comparison, traditional diets may require significant willpower and self-control, making them a less effective option for sustainable weight loss.
Moreover, bariatric surgery can impact your metabolism, the process by which your body converts calories from food into usable energy. A higher metabolism allows you to burn more calories, even at rest. Research has shown that metabolic rates can increase after bariatric surgery, leading to a more efficient calorie-burning process. In contrast, diets may cause your metabolism to slow down as your body tries to conserve energy, making weight loss more difficult in the long run.
Another important aspect to consider is hormonal changes. Bariatric surgery has been found to regulate appetite-controlling hormones such as ghrelin and leptin. By altering the levels of these hormones, surgery can reduce hunger, promote satiety, and make it easier for you to control your caloric intake. Traditional diets might not have the same impact on these hormones, leaving you feeling hungry and less satisfied with your meals.
Finally, bariatric surgery can have positive effects on your lifestyle and behavior. After the procedure, you are usually encouraged to adopt healthier habits, such as exercising regularly and making better food choices. These new habits can further contribute to weight loss success. Dieting alone might not have the same impact, as the focus is often more narrowly aimed at counting calories or eliminating certain foods and not necessarily making broader changes to improve overall health.
When considering the difference between bariatric surgery and traditional diets, it becomes clear why surgery has higher long-term success rates. Not only does it affect the anatomy of your gastrointestinal system and metabolism, but it also influences hormonal balances and encourages healthier lifestyle changes. While diets might work temporarily, the comprehensive approach of bariatric surgery can make it a more effective and lasting solution for weight loss.
Also Read: 11 Complications After Gastric Bypass And Prevention Strategies